User Acceptance: Clinical Virtual Simulation in Nursing Education
Due to technological and scientific advancements, there has been a significant transformation in Health Education. Institutions face the ongoing challenge of innovating teaching methods to ensure theoretical knowledge translates into practical clinical skills.
However, bridging this gap, especially in clinical decision-making, remains a significant barrier for educators and students.
Clinical Virtual Simulation: Predictors of user acceptance
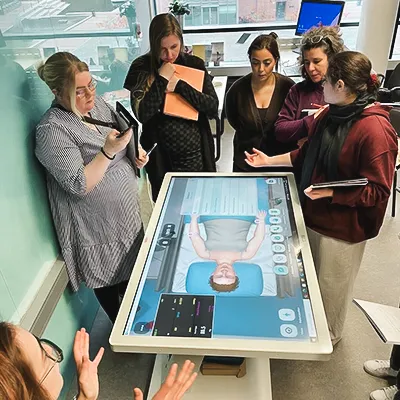
Padilha, Costa, and Ferreira (2024) conducted a study involving 619 nursing students discovering essential insights into how nursing students perceive and use Clinical Virtual Simulation (CVS) in their education process.
Two factors emerged as key in shaping nursing students’ attitudes toward virtual simulation: the relevance of learning and the enjoyment, both crucial in the interplay between educational experiences and technological advancements in healthcare training.
The study suggests that these external factors play a crucial role in shaping students’ acceptance and utilization of virtual simulation in Nursing Education. Moreover, it also elucidates that significant proportions of these aspects are explained by the interplay between internal constructs and external determinants, highlighting the multifaceted nature of students’ perceptions and attitudes toward innovative educational tools.
By delving into the nuanced dimensions of CVS acceptance, the study offers valuable insights for educators, curriculum designers, and policymakers in Nursing Education.
Recognizing the importance of relevance for learning and enjoyability, schools can implement platforms like Body Interact to tailor educational interventions and technological innovations while meeting the needs and preferences of their students’ community.
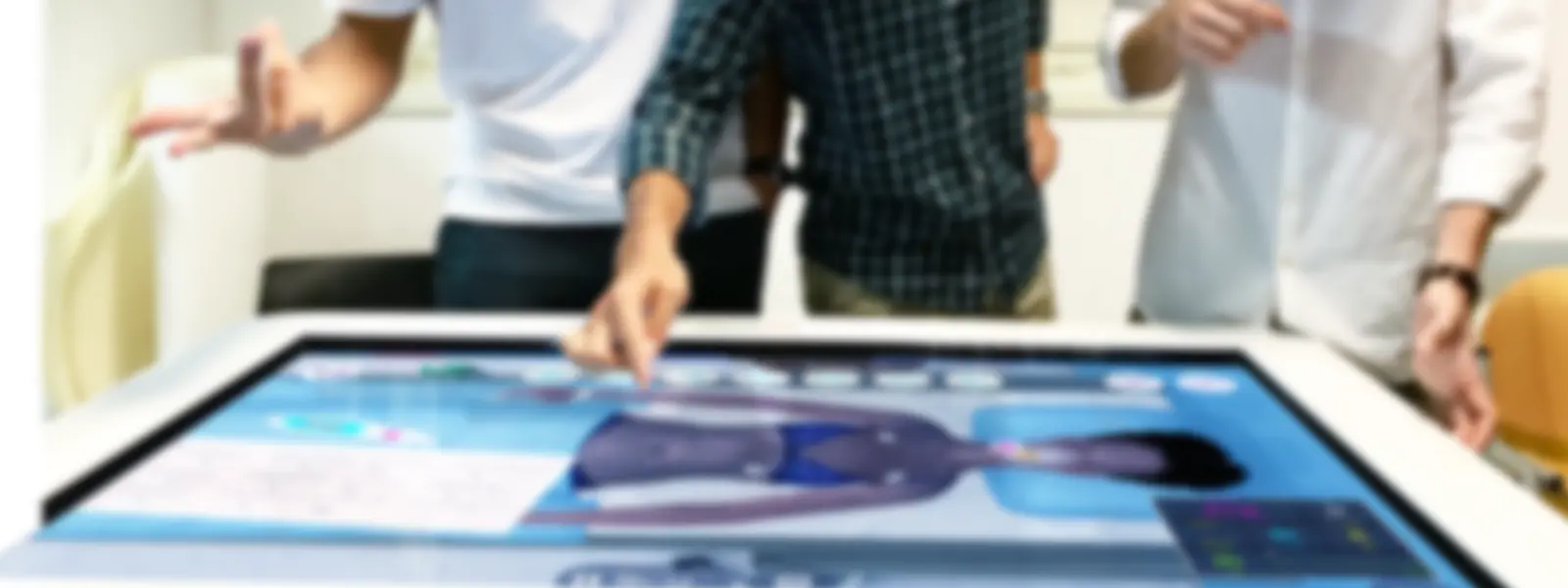
Body Interact in Advancing Clinical Virtual Simulation
The study provides a foundation for future research and development efforts aimed at enhancing the effectiveness and efficiency of virtual simulation in nursing education.
With its immersive and interactive approach, Body Interact holds promise as a valuable tool in preparing future generations of nurses for the challenges of real-world clinical practice.
In conclusion, the study enhances our understanding of clinical virtual simulation’s acceptance in nursing education. Emphasizing the significance of relevance for learning and enjoyability, it provides valuable direction for schools. These insights drive ongoing advancements in nursing education, ensuring future nurses are prepared to excel in dynamic healthcare settings. With platforms like Body Interact leading the way, nursing education continues to evolve, nurturing skilled professionals for real-world clinical practice.
Are you interested in reviewing other research papers?
Visit our International Research Studies page. Explore Body Interact educational impact.
By Ana Santa – MSN, APRN