From Simulation to Real-world: Bridging the Gap in Nursing Education
Nursing education has made significant progress in preparing students for the unpredictable nature of real-world healthcare. One of the major problems of nursing education is the insufficient coordination between theory and practice. [1]
In this article, we´ll explore how Body Interact, the virtual patient simulator, is an excellent tool to help the transition from theory to real-world scenarios smoother for nursing students.
The Need for Realism
Traditional simulations have been a staple in nursing education, but realism has often been a missing piece. According to evidence, providing educational experiences that will expose nurses to realistic clinical scenarios at an undergraduate level is one way of increasing experiential knowledge, improving the transition to practice. [2] [3]
Pedagogical strategies, such as immersive simulation experiences, create a space for students to engage in reflective practices during and after actions. This enables the demonstration of critical thinking, the acquisition of new knowledge and skills, and the development of strategic approaches. [3]
How Body Interact Bridges the Gap in nursing education
- Highly realistic virtual environment
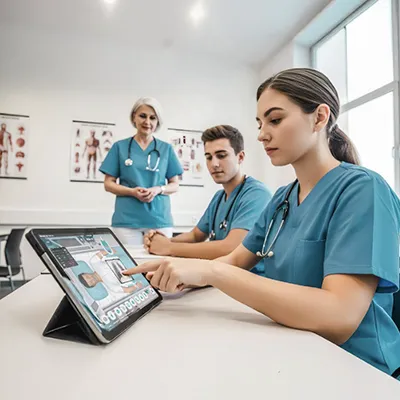
Simulation has been shown to bridge the gap between theory and practice. [4] Body Interact steps in to address this gap, offering a highly realistic virtual environment where students can interact with lifelike patients.
Body Interact doesn’t just mimic clinical situations – it replicates them in detail. The simulator provides a diverse range of scenarios covering various medical specialties, helping students build a comprehensive skill set that’s applicable in real-world healthcare settings. The realistic and dynamic environment allows nursing students to interact with lifelike virtual patients, facing a wide array of clinical challenges and scenarios.
Transitioning from simulated scenarios to real-world challenges can be scary, but Body Interact serves as a bridge to ease this process.
- Developing Critical thinking
Critical thinking is a crucial skill in the nursing profession, so teaching strategies and methodology must be carefully considered when training and preparing nursing students to think critically.[6] Body Interact challenges students to think on their feet and make decisions in real-time, fostering the quick and effective decision-making skills crucial for nursing practice.
- Teamwork in Focus
Acknowledging the significance of teamwork in healthcare, Body Interact integrates collaborative features, enabling students to hone their communication and teamwork skills within a multidisciplinary team crucial for providing effective patient care. Using Body Interact, students can engage in dialogues with patients and their families, and reach out to various specialties, fostering a collaborative approach to teamwork.
- Feedback and Debriefing
After completing a simulation, Body Interact provides a structured debriefing process where participants from different disciplines can discuss the outcomes, share perspectives, and receive feedback. This debriefing helps enhance communication, identify areas for improvement, and promote continuous learning.
- Integration of Theory and Practice
By immersing students in realistic scenarios, simulation helps bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application. This integration is crucial for preparing nursing students for the complexities of real-world healthcare
Conclusion
Body Interact provides high-fidelity and immersive experiences that prepare students for real-world healthcare, allowing them to be more confident and competent. As nursing students graduate with skills honed in realistic virtual scenarios, the future of healthcare looks promising with a new wave of well-prepared nurses.
Learn more about Body Interact here!
References:
[1] Koukourikos K, Tsaloglidou A, Kourkouta L, Papathanasiou IV, Iliadis C, Fratzana A, Panagiotou A. Simulation in Clinical Nursing Education. Acta Inform Med. 2021 Mar;29(1):15-20. doi: 10.5455/aim.2021.29.15-20. PMID: 34012208; PMCID: PMC8116070.
[2] Tan, Kimberly-Ann & Seah, Betsy & Lai Fun, Wong & Lee, Cindy & Goh, Sam & Liaw, Sok. (2022). Simulation-Based Mastery Learning to Facilitate Transition to Nursing Practice. Nurse Educator. Publish Ahead of Print. 10.1097/NNE.0000000000001224.
[3] – Hayes C. Simulation: Smoothing the transition from undergraduate to new graduate. J Nurs Manag. 2018 Jul;26(5):495-497. doi: 10.1111/jonm.12676. PMID: 30917209.
[4]Rutherford-Hemming T. et al. The Use of Simulation-Based Education With New Graduate Nurses in Emergency Department and Acute Care Settings: A Scoping Review. The Journal of Continuing Education in Nursing, 2022;53(7):301–306. doi.org/10.3928/00220124-20220603-05
[5] Alshehri FD, Jones S, Harrison D. The effectiveness of high-fidelity simulation on undergraduate nursing students' clinical reasoning-related skills: A systematic review. Nurse Educ Today. 2023 Feb;121:105679. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2022.105679. Epub 2022 Dec 5. PMID: 36542870.
[6]Stenseth H, Steindal S, Solberg M, Ølnes M, Mohallem A, Sørensen A, Strandell-Laine C, Olaussen C, Aure C, Riegel F, Pedersen I, Zlamal J, Martini J, Bresolin P, Linnerud S, Nes A Simulation-Based Learning Supported by Technology to Enhance Critical Thinking in Nursing Students: Protocol for a Scoping Review JMIR Res Protoc 2022;11(4):e36725. 10.2196/36725