Unveiling the Power of Serious Games and Gamification
In the constant evolution of the healthcare world, it is essential to become up-to-date with the latest teaching methods. Recent research has shone the landscape of serious games and gamification in healthcare education, enlightening their effectiveness, and future potential.
In this article, we will explore the valuable insights from these growing tools.
Healthcare Professionals’ Perspective on Serious Games in Education
The investigation into healthcare professionals’ perspectives across diverse age groups and occupations concerning serious games as an instructional tool produced surprising results.
Astonishingly, the majority of healthcare practitioners displayed limited familiarity with these pioneering pedagogical tools, with fewer than 10% reporting any prior exposure to them.[1] This revelation hints at the limited integration of serious games in the education of physicians, nurses, and other healthcare practitioners.
Even though this new technology might not yet be widely recognized among professionals, the integration of simulation into medical education has demonstrated positive impacts on knowledge and skill acquisition, as well as patient outcomes.[2] Consequently, serious gaming, which is included in the broader domain of simulation, is prepared to take on a more prominent role in healthcare education.
The Impact on Health Professionals
Incorporating serious gaming or gamification into both pre- and post-graduation health professions education leads to enhanced knowledge, skills, and overall satisfaction compared to conventional educational methods and possibly other forms of digital education. [3]
Serious games are providing interactive digital experiences that improve learning, enhance knowledge retention, and refine clinical decision-making skills. Their potential to revolutionize healthcare training not only increases job satisfaction among providers but also contributes to more effective and adaptable healthcare education and practice. [2]
Future Directions in Healthcare Education
As we look to the future of healthcare education, the emergence of serious games and gamification provides alternative approaches for educators to improve the medical teaching process. [4]
With ongoing advancements in technology, including virtual patients, the potential for creating even more realistic and immersive learning experiences is limitless.
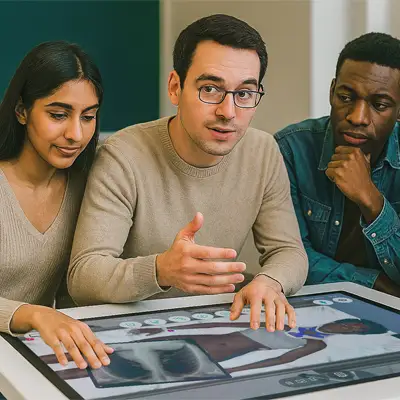
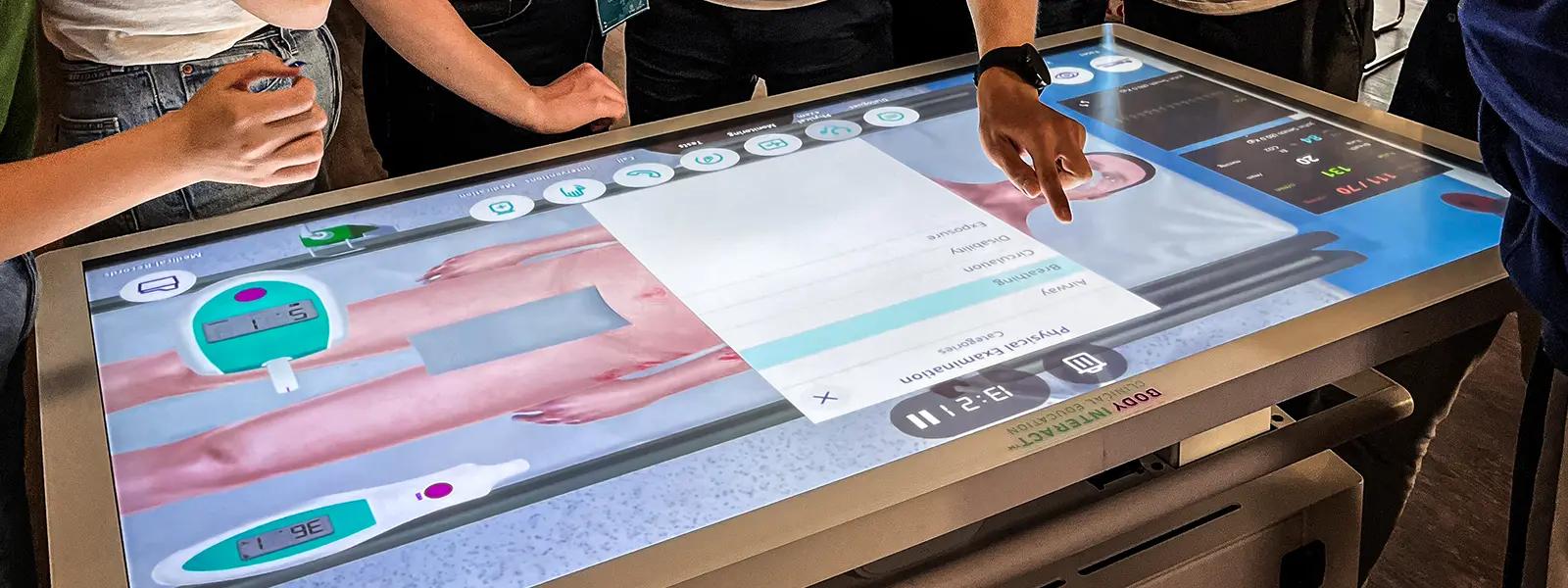
Body Interact is a state-of-the-art, immersive serious game designed specifically for healthcare education. It places healthcare professionals in realistic clinical scenarios where they must diagnose and treat virtual patients. The game’s lifelike simulations provide a safe and risk-free environment for learners to practice and improve their clinical skills, making it an invaluable tool for medical, nursing, and allied healthcare training.
Conclusion
These innovative tools, like Body Interact, offer a dynamic and effective way to bridge the gap between theory and practice, preparing healthcare professionals to excel in their careers and ultimately improve patient care.
As the healthcare field continues to evolve, embracing tools like Body Interact will be crucial in ensuring that healthcare professionals are not only well-informed but also well-prepared to meet the ever-changing demands of their professions. Serious games and gamification are not just the future; they are the present of healthcare education.
References
- Katonai Z, Gupta R, Heuss S, Fehr T, Ebneter M, Maier T, Meier T, Bux D, Thackaberry J, Schneeberger AR. Serious Games and Gamification: Health Care Workers’ Experience, Attitudes, and Knowledge. Acad Psychiatry. 2023 Apr;47(2):169-173. doi: 10.1007/s40596-023-01747-z. Epub 2023 Jan 26. PMID: 36703089; PMCID: PMC9879618.
- Wang, Ryan BA; DeMaria, Samuel Jr MD; Goldberg, Andrew MD; Katz, Daniel MD. A Systematic Review of Serious Games in Training Health Care Professionals. Simulation in Healthcare: The Journal of the Society for Simulation in Healthcare 11(1):p 41-51, February 2016. | DOI: 10.1097/SIH.0000000000000118
- Gentry SV, Gauthier A, L’Estrade Ehrstrom B, Wortley D, Lilienthal A, Tudor Car L, Dauwels-Okutsu S, Nikolaou CK, Zary N, Campbell J, Car J. Serious Gaming and Gamification Education in Health Professions: Systematic Review. J Med Internet Res. 2019 Mar 28;21(3):e12994. doi: 10.2196/12994. PMID: 30920375; PMCID: PMC6458534.
- Xu M, Luo Y, Zhang Y, Xia R, Qian H, Zou X. Game-based learning in medical education. Front Public Health. 2023 Mar 3;11:1113682. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1113682. PMID: 36935696; PMCID: PMC10020233.
- Damaševičius R, Maskeliūnas R, Blažauskas T. Serious Games and Gamification in Healthcare: A Meta-Review. Information. 2023; 14(2):105. https://doi.org/10.3390/info14020105